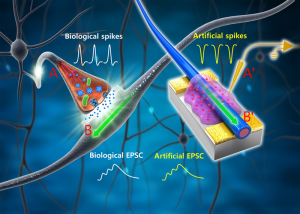
South Korean scientists from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at Pohang University of Science and Technology appear to have cleared the largest obstacle to the feasibility of building brain-like computers: power consumption. In their paper “Organic core-sheath nanowire artificial synapses with femtojoule energy consumption,” published in the June 17th edition of Science Advances, …
Tag: neurons
May 08 2016
Neural Networks: The Node
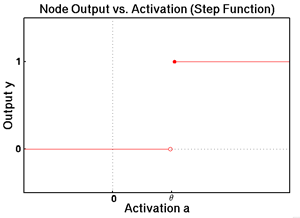
As I covered previously in “Introduction to Neural Networks,” artificial neural networks (ANN) are simplified representations of biological neural networks in which the basic computational unit known as an artificial neuron, or node, represents its biological counterpart, the neuron. In order to understand how neural networks can be taught to identify and classify, it is first …
Mar 10 2016
Introduction to Neural Networks
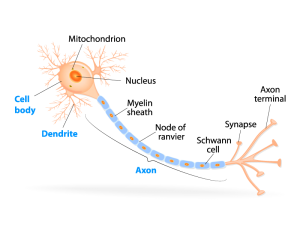
Modeled after observed biology and behavior within the brain, neural networks are arguably the most popular of the biologically inspired AI methods. Neural networks excel at pattern recognition and classification tasks including facial, speech, and handwriting recognition. They also often play a central role in video game character AI.
Mar 27 2006
European Researchers Create Neuro-Chip
Both LiveScience.com and New Scientist are reporting today that a team of Italian and German neuroscientists working in conjunction with mobile chip maker Infineon have created a “neuro-chip,” a hybrid microchip that interfaces living neurons with traditional silicon circuitry. In addition to providing new insights into the brain’s inner workings, the groundbreaking work could one …
Feb 24 2006
Synchronized Neurons Focus Attention
According to a study published recently in Nature, neurons firing synchronously help to focus the brain’s attention on certain tasks and lead to quicker response times. When neurons fire independently their electrical output is nothing but noise, and no coherent signal is discernible in the static. When even a few neurons fire synchronously, their individual …
Jan 20 2006
How the Brain Reassembles Visual Input
It happens automatically and so quickly that most people probably never question the process of vision. Although it starts with the eyes, the majority of the work is performed in stages by cooperating layers of neural regions in the brain. As such, the underlying mechanism behind seeing and recognizing objects has long been of interest …
Jan 13 2006
Cilia Direct Newborn Adult Brain Cell Migration
Neuroscientists have never fully understood how new adult brain cells are able to traverse the relatively long distances they need to cover in order to reach their final locations within the brain. LiveScience.com is reporting today that a recent study of mouse brains co-authored by researchers at the University of California, San Francisco sheds some …
Jan 06 2006
Astrocytes Can Independently Control Blood Flow
Astrocytes, also known as astroglia, are star-shaped cells in the brain whose function and importance has never been fully understood by neuroscientists. Once thought to be housekeeping cells under the control of neurons, LiveScience.com is reporting today that researchers have found that astrocytes can directly and independently perform the critical function of controlling blood flow …
Dec 28 2005
Neuron Growth Occurs in Adult Brains
Researchers from the Picower Institute for Learning and Memory at MIT have recently found that contrary to popular belief, neurons do grow in mature brains. It had been widely accepted that structural remodeling of neurons does not occur in adult brains, but the discovery that it does could lead to advances in treatments of spinal …
Dec 20 2005
Retrograde Signal Strengthens Synapses
Researchers from MIT studying brain plasticity, the reorganization of brain cells and their connections over time, have recently discovered a “backtalk” or retrograde signal from post-synaptic to pre-synaptic neurons that plays a crucial role in synapse development. It has long been known that synaptic strength, the strength of the connections between neurons, plays a central …
- 1
- 2